“Running a project without a Work Breakdown Structure is like going to a strange land without a road map.”
J. Phillips
Like a map for the explorer, the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) represents the reference structure for the project team to visualize the work to be completed to achieve the project objectives.
The WBS, in fact, allows representing the entire project scope, decomposing it hierarchically into smaller and smaller blocks. t is conventionally represented as an inverted tree: the trunk identifies the project as a whole, while the branches progressively represent the smaller components of the project.
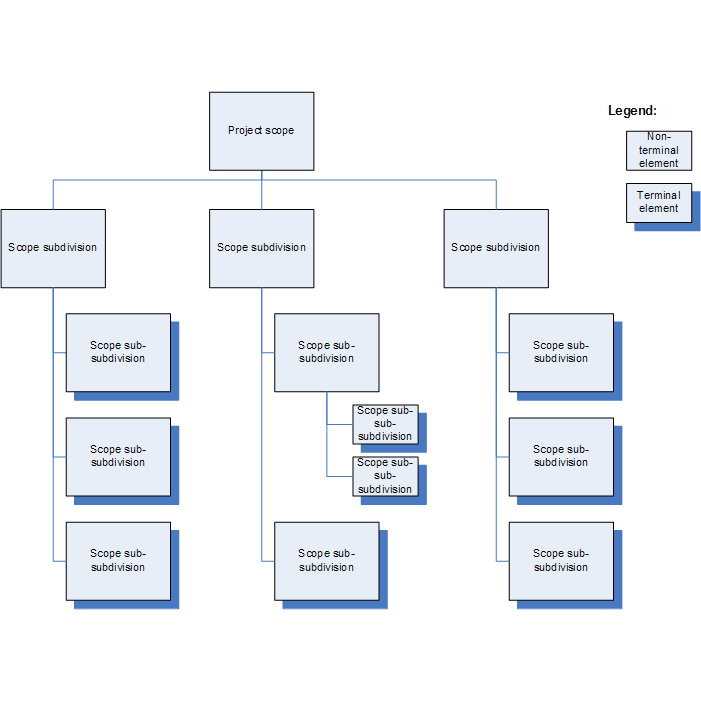
This simple structure highlights a fundamental concept: the WBS is not a list of the project's elementary activities. It is oriented to the decomposition of the scope into deliverables. The PMBOK® Guide specifies: "In the context of the WBS, work refers to products or deliverables that are the result of effort and not to the effort itself."
The activities can only be identified by further breaking down the most elementary parts of the WBS: the Work Packages (WPs)
The WPs, located in the lowest level of the hierarchical structure, aggregate those parts of the project work that can be assigned to a single business function, organizational unit, cost centers, or similar.
The WBS creation process
“Create WBS is the process of subdividing project deliverables and project work into smaller, more manageable components. It provides a structured vision of what has to be delivered. ”
(A Guide to the Project Management Body Of Knowledge – Sixth edition, ©2017 Project Management Institute, Inc.)
To create the WBS, the PMBOK identified four main inputs:
- the Project Management Plan and, in detail, the Scope management plan;
- project documentation, such as Scope statement and Requirements documentation;
- Environmental Enterprise Factors;
- Organizational Process Assets.
Analizziamoli individualmente e vediamo come possono esserci d’aiuto.
| Input | Description |
| Scope management plan | It identifies how the project's scope will be defined, developed, monitored, controlled, and validated. Therefore, the Plan should include directions for creating the project's WBS. |
| Scope statement | It describes the product, service, or result of the project, establishing its limits and acceptance criteria. We create the WBS by breaking down what is inserted in this document. |
| Requirements documentation | To create the WBS, we must consider the business requirements, stakeholders' requirements, requirements for the product/solution, and the project. |
| Environmental Enterprise Factors | In the project-related sector, specific WBS standards may be in place. |
| Organizational Process Assets | Our organization may already have WBS policies, procedures, or templates to consider. Furthermore, we could draw on Lessons Learned from previous projects to anticipate a problem that has already occurred in the work breakdown or to integrate a good practice that emerged previously. |
How to structure the WBS
There is no single WBS model: it is possible to structure it, among other things, by project phases, main deliverables, or areas of activity. The important thing is that the scope is broken down to a level that allows an accurate estimate and management of costs and times. Lower-level elements need to be sufficient to complete the deliverables of the higher level.
An essential structure can be defined as follows:
- I Level - Project title
- II Level - Main deliverables (essential to achieving the project objectives)
- III Level - Work Packages (the breakdown of the main deliverables into the elements necessary to complete them)
Example
We are the project manager of XYZ company for the QWERTY project. The project responds to the need to train employees on the use of new management software. Now, we need to create the WBS.
Let's go directly to the inputs:
- the Scope management plan defines that, to manage the work needed to complete this project effectively, the scope will be divided into individual WPs of min. 4 to the max. 40 hours each;
2. in the Scope statement we identify that the project is aimed at training employees on the new management system and responds to the organization's need to manage its facilities more effectively, and the main deliverables are
- an E-learning Platform to deliver training courses to employees on how to use the new software, and
- a User Manual to facilitate the navigation and use on the platform;
3. in the Requirements documentation it is established that the project must make use of only internal resources and, therefore, internal developers should be in charge of the e-learning platform;
4. there are no industry standards or WBS models within the organization that can or must be used as references.
Once we have the information collected, our WBS could be basically defined as follows:
1. QWERTY
1.1 E-Learning Platform
1.1.1 Course Modules
1.1.2 Infrastructure
1.1.3 Tests
1.2 User Manual
1.2.1 Contents
1.2.2 Layout
1.2.3 Presentation